Abstract
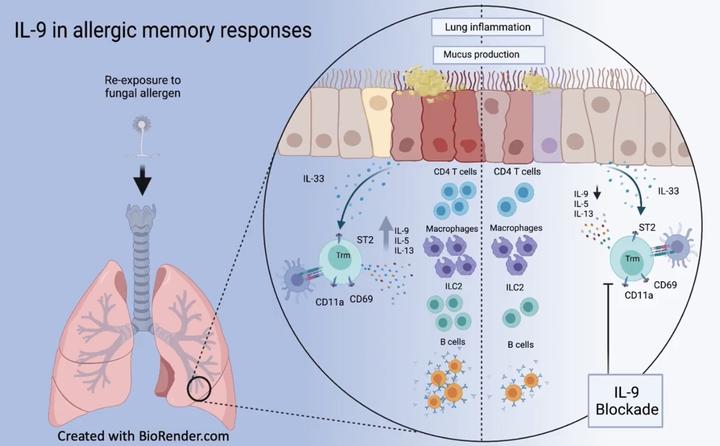
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory lung disease with intermittent flares predominately mediated through memory T cells. Yet, the identity of long-term memory cells that mediate allergic recall responses is not well defined. In this report, using a mouse model of chronic allergen exposure followed by an allergen-free rest period, we characterized a subpopulation of CD4+ T cells that secreted IL-9 as an obligate effector cytokine. IL-9–secreting cells had a resident memory T cell phenotype, and blocking IL-9 during a recall challenge or deleting IL-9 from T cells significantly diminished airway inflammation and airway hyperreactivity. T cells secreted IL-9 in an allergen recall–specific manner, and secretion was amplified by IL-33. Using scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq, we defined the cellular identity of a distinct population of T cells with a proallergic cytokine pattern. Thus, in a recall model of allergic airway inflammation, IL-9 secretion from a multicytokine-producing CD4+ T cell population was required for an allergen recall response.
Supplementary notes can be added here, including code, math, and images.